m (Remove some templates. interwiki linksnd move Wikipedia link above categories) |
m (Delink some non military terms and remove some templates) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
| partof = [[World War II]], [[Pacific War]] |
| partof = [[World War II]], [[Pacific War]] |
||
| date = 31 January-3 February 1944 |
| date = 31 January-3 February 1944 |
||
| − | | place = |
+ | | place = Kwajalein Atoll, [[Marshall Islands]] |
| result = United States victory |
| result = United States victory |
||
| combatant1 = {{flagicon|USA|1912}} [[United States]] |
| combatant1 = {{flagicon|USA|1912}} [[United States]] |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
| − | The '''Battle of Kwajalein''' was fought as part of the [[Pacific War|Pacific campaign]] of [[World War II]]. It took place from 31 January-3 February 1944, on |
+ | The '''Battle of Kwajalein''' was fought as part of the [[Pacific War|Pacific campaign]] of [[World War II]]. It took place from 31 January-3 February 1944, on Kwajalein Atoll in the [[Marshall Islands]]. Employing the hard-learned lessons of the [[battle of Tarawa]], the United States launched a successful twin assault on the main islands of Kwajalein in the south and [[Roi-Namur]] in the north. The Japanese defenders put up stiff resistance, although outnumbered and under-prepared. The determined defense of Roi-Namur left only 51 survivors of an original garrison of 3,500. |
For the US, the battle represented both the next step in its [[Leapfrogging (strategy)|island-hopping]] march to Japan and a significant moral victory because it was the first time the Americans had penetrated the "outer ring" of the Japanese Pacific sphere. For the Japanese, the battle represented the failure of the beach-line defense. Japanese defenses became prepared in depth, and the battles of Peleliu, [[Guam]], and the Marianas proved far more costly to the US. |
For the US, the battle represented both the next step in its [[Leapfrogging (strategy)|island-hopping]] march to Japan and a significant moral victory because it was the first time the Americans had penetrated the "outer ring" of the Japanese Pacific sphere. For the Japanese, the battle represented the failure of the beach-line defense. Japanese defenses became prepared in depth, and the battles of Peleliu, [[Guam]], and the Marianas proved far more costly to the US. |
||
Revision as of 16:55, 3 August 2014
The Battle of Kwajalein was fought as part of the Pacific campaign of World War II. It took place from 31 January-3 February 1944, on Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands. Employing the hard-learned lessons of the battle of Tarawa, the United States launched a successful twin assault on the main islands of Kwajalein in the south and Roi-Namur in the north. The Japanese defenders put up stiff resistance, although outnumbered and under-prepared. The determined defense of Roi-Namur left only 51 survivors of an original garrison of 3,500.
For the US, the battle represented both the next step in its island-hopping march to Japan and a significant moral victory because it was the first time the Americans had penetrated the "outer ring" of the Japanese Pacific sphere. For the Japanese, the battle represented the failure of the beach-line defense. Japanese defenses became prepared in depth, and the battles of Peleliu, Guam, and the Marianas proved far more costly to the US.
Background
Geography
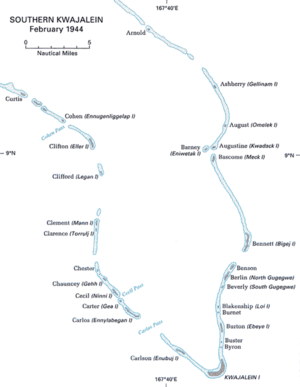
Kwajalein Atoll is in the heart of the Marshall Islands. It lies in the Ralik Chain, 2,100 nmi (2,400 mi; 3,900 km) southwest of Honolulu, Hawaii at 8°43′N 167°44′E / 8.717°N 167.733°E. Kwajalein is the world's largest coral atoll as measured by the area of enclosed water. Comprising 97 islets, it has a land area of 1,560 acres (6.33 km²) and surrounds one of the largest lagoons in the world, measuring 324 mi² (839 km²) in size.
The two most significant land masses are Kwajalein Island in the south, and the linked islands of Roi-Namur in the north. By the start of World War II, the Marshalls (South Pacific Mandate) were already an integral part of the Japanese perimeter of defense. Its facilities were being utilized as outlying bases for submarines and surface warships, as well as for air staging for future advances being planned against Ellice, the Fiji Islands, and Samoa.
Gilbert and Marshall Islands campaign
After the capture of Makin and Tarawa in the Gilbert Islands, the next step in the United States Navy's campaign in the central Pacific was the Marshall Island chain. These islands had been German colonies until World War I, when they were assigned to Japan in the post-war settlement as the "Eastern Mandates". The islands had become a mystery since the Japanese closed them to the outside world. It was presumed the Japanese had built illegal fortifications throughout the islands, however the precise extent of any such fortifications was unknown. To the Japanese, regarding them as part of the "outer ring" of Japanese territory held prior to 1941, this assault would be the first on what the Japanese regarded as Japanese soil.
The strategic importance of the Marshalls had been identified as early as 1921 in Plan Orange—the American interwar plan for a possible conflict with Japan. The Marshalls were a key step in the island-hopping march to mainland Japan.
After the loss of the Solomon Islands and New Guinea to the Allies in 1943, the Japanese command decided that the Gilbert and Marshall Islands would be expendable. They preferred to fight a decisive battle closer to home. However, at the end of 1943, the Marshalls were reinforced to make their taking expensive for the Americans. By January 1944, the regional commander in Truk—Admiral Masashi Kobayashi—had 28,000 troops to defend the Marshalls, but he had very few planes.
Japanese planning and preparations
Actual defenses on the Marshalls, however, were never very substantial or heavily manned. After nearly 10 years of construction, fortifications on the Marshalls were considerably inferior[citation needed] when compared with Tarawa, which had been turned into a fortress in less than eighteen months.
Furthermore, less than half of the troops stationed in the Marshalls were combat trained,[citation needed] the rest being support and labor troops with little or no combat training. It was not until after the Japanese position in the Solomons and New Guinea began to deteriorate that Imperial Headquarters made plans to strengthen the Marshalls. In fact, by September 1943, the Japanese High Command had written off the Gilberts and Marshalls as lost, deciding that the areas should be used to fight a delaying action while a new defense perimeter was created from the Banda Sea through Caroline Island and the Marianas Islands. Additionally, combat units were ordered to the Marshalls from the Philippines, Manchukuo, and the homeland, with additional air power to be flown in from both the homeland and nearby Truk.
The 6th Base Force, under the command of Rear Admiral Monzo Akiyama, and headquartered on Kwajalein, was the principal defense force of the islands. Akiyama, however, had his men spread out over a very wide area, mostly concentrating on the defense of those atolls (Jaluit, Mille, Maloelap, and Wotje), that were never considered vulnerable to American attack. Those reinforcement troops included 2nd Battalion/1st Amphibious Brigade under Captain (Naval) Aso, nine Type 94/97 Tankettes and two companies of Type 2 Amphibious Tank (in the Japanese Special Naval Landing Forces (SNLF)), or Kwajalein Tank Detachment). They finally arrived and were quickly dispersed by Akiyama, mainly to the outlying atolls.
Kwajalein was to remain undermanned, underequipped, and unprepared for the assaults being arrayed against it. Overall Japanese strength on these islands numbered approximately 8,000 men, of which less than half were considered combat effective. On Kwajalein proper, the troops were made up mostly of labor forces, a good number of those being Koreans. On Roi-Namur, the troops were mostly JNAF land personnel who had little ground combat training and who were underequipped for such a function.[citation needed]
The defense system on the islands was mostly in line, with little or no depth. Although some fortified areas existed, none were as extensive or well armed as those of Tarawa. In addition, there were several defenses that mostly concentrated on any assault coming from the ocean side; no coastal defense artillery had been placed on key islets guarding passages to the lagoon, and there was little or no use of mines. Despite shortfalls, efforts to strengthen ground defenses continued. Still, Akiyama's greatest defense remained in his aerial offensive capability. He had well-manned air bases on Roi-Namur, Maloelap, Wotje, Mille and Eniwetok, detached Chitose and 653rd Air Corps Mitsubishi A6M Zero fighters with the nearly complete Mitsubishi G3M and G4M bomber base in Kwajalein. In addition, he had some Nakajima A6M2-N and Mitsubishi F1M floatplanes detached in seaplane bases on Jaluit, Wotje, Majuro, Taongi, Utirik, and the south Kwajalein Atoll island of Burton.
During the month of November, however, both USAAF land-based and US Navy carrier-based bomber attacks, in conjunction with the American assault on the Gilberts, had destroyed 71 of Akiyama's fighters and bombers. Reinforcements flown in from the homeland and Truk replenished most of his losses, but he could expect little additional help in the future. The Japanese war industry was falling far short of needed production, affecting all branches of the armed services, including the Japanese Carrier Air Arm, which had long since retreated from the Central Pacific. In fact, the 32 planes flown from Truk were the last of the carrier aircraft left behind following that retreat. Akiyama was therefore not expected to defeat his adversary, but rather to delay the Allied forces advance while exacting the greatest possible toll upon them.
US planning and preparation
Expecting the US to attack the outermost islands in the group first, most of the defenders were stationed on the atolls of Wotje, Mille, Maloelap, and Jaluit to the east and south. Indeed, the original American plan called for a cautious series of steppingstone attacks starting in the eastern Marshalls. The Japanese troop dispositions were revealed to the Americans by Ultra decryptions of Japanese communications; Admiral Chester Nimitz, commander of American naval forces in the Pacific, decided to bypass these outposts and attack the Kwajalein Atoll directly, knifing into the very heart of the Marshall Islands. The operation was given the code name Operation Flintlock.
There were two main objectives: The linked islands of Roi-Namur in the north, and Kwajalein Island at the southern end of the atoll. The 4th Marine Division—under Major General Harry Schmidt—was assigned to Roi-Namur, and the Army's 7th Infantry Division—under Major General Charles H. Corlett—would make the assault on Kwajalein.
To ensure the success of the operation, sea and air superiority were necessary. Accordingly, on 29 January 1944, US carrier planes attacked the Japanese airfield on Roi-Namur, destroying 92 of the 110 Japanese planes in the Marshalls.
Staging through Baker Island airfield, B-24 Liberators of the Seventh Air Force quickly set their sights upon their targets. In the beginning, the most important was Mili Atoll, the Japanese base closest to the Gilberts and Maloelap, the most powerful enemy bases threatening the upcoming operations. Mille was the subject of several attacks throughout November, causing considerable damage to installations and high losses of aircraft for the Japanese. But Mille remained the only base within fighter reach of the Gilberts, and the defenders managed to keep the facilities there operational and reinforced with aircraft. Following the capture of Tarawa and until 19 December, 106 B-24s dropped a total of 122 short tons (111 t) of explosives on Mille's airbase. The largest of those raids came on 4 December when 34 B-24s pulverized the atoll in conjunction with carrier-based bombing raids of other parts of the Marshalls. On 18 December, renewed strikes were initiated against enemy targets on Mille with land-based Douglas A-24 Banshee dive bombers and Bell P-39 Airacobra fighters making their debut in the Marshall air offensive. Japanese losses for the day amounted to 10 fighters (four on the ground) and four damaged. Other aircraft types participating in the offensive included B-25 Mitchells and Curtiss P-40 Warhawks.
In addition, it was necessary to take another atoll in the eastern Marshalls—Majuro. This feature is 220 mi (190 nmi; 350 km) southeast of Kwajalein and could serve as an advanced air and naval base as well as safeguard supply lines to Kwajalein. Majuro was very lightly defended and only the V Amphibious Corps Marine Reconnaissance Company and the 2nd Battalion, 106th Infantry, 7th Infantry Division were employed in its capture. The island was taken on 31 January 1944, without any US casualties.

Kwajalein Atoll, 2 February 1944: Private First Class N. E. Carling stands beside the medium tank "Killer" on which is mounted a knocked-out Japanese light tank. The American tank is an M4 Sherman, the Japanese vehicle is a Type 94 tankette.
Battle
The US forces for the landings were Rear Admiral Richmond K. Turner's 5th Amphibious Force, and Major General Holland M. Smith's V Amphibious Corps, which comprised the 4th Marine Division commanded by Maj. Gen. Harry Schmidt, the 7th Infantry Division commanded by Maj. Gen. Charles H. Corlett, plus the 22nd Marines, 106th Infantry, and the 111th Infantry regiments. The 4th and 7th Divisions were assigned to the initial landings at Kwajalein, while the 2nd Battalion of the 106th was assigned to the simultaneous capture of Majuro Atoll. The rest of the 106th and the 22nd Marines were in reserve for Kwajalein, while awaiting the following assault on Eniwetok, scheduled for three months later.
The 7th Infantry Division began by capturing the small islands labeled Carlos, Carter, Cecil, and Carlson on 31 January, which were used as artillery bases for the next day's assault. Kwajalein Island is 2.5 mi (4.0 km) long but only 880 yd (800 m) wide. There was therefore no possibility of defence in depth, so the Japanese planned to counter-attack the landing beaches. They had not realized until the battle of Tarawa that American amphibious vehicles could cross coral reefs and so land on the lagoon side of an atoll; accordingly the strongest defences on Kwajalein faced the ocean. The bombardment by battleships, B-24 bombers from Apamama and artillery on Carlson was devastating. The US Army history of the battle quotes a participant as saying that "the entire island looked as if it had been picked up 20,000 feet and then dropped." By the time the 7th Division landed on Kwajalein Island on 1 February, there was little resistance; by night the Americans estimated that only 1,500 of the original 5,000 defenders were still alive.
On the north side of the atoll, the 4th Marine Division followed the same plan, first capturing islets Ivan, Jacob, Albert, Allen, and Abraham on 31 January, and landing on Roi-Namur on 1 February. The airfield on Roi (the eastern half), was captured quickly, and Namur (the western half), fell the next day. The worst setback came when a Marine demolition team threw a satchel charge of high explosives into a Japanese bunker which turned out to be a torpedo warhead magazine. The resulting explosion killed twenty Marines and wounded dozens more.[1] Only 51 of the original 3,500 Japanese defenders of Roi-Namur survived to be captured.
Aftermath

SecNav Frank Knox presented with the flag that flew over Kwajalein, 1944
The relatively easy capture of Kwajalein demonstrated US amphibious capabilities and showed that the changes to training and tactics after the bloody battle of Tarawa had been effective. It allowed Nimitz to speed up operations in the Marshalls and invade Eniwetok Atoll on 17 February 1944.
The Japanese learned from the battle that beachline defenses were too vulnerable to bombardment by ships and planes. In the campaign for the Mariana Islands, the defense in depth on Guam and Peleliu was much harder to overcome than the thin line on Kwajalein.
Notes
- ↑ Duncan, Basil. "Roi-Namur". THE MARSHALL ISLANDS CAMPAIGN. http://www.geocities.com/Heartland/Plains/5850/marshalls.html. Retrieved 14 February 2013.
References
- Bailey, Dan E. (1992). World War II: Wrecks of the Kwajalein and Truk Lagoons. North Valley Diver Publications. ISBN 0-911615-05-9.
- Marshall, S. L. A.; Joseph G. Dawson (2001). Island Victory: The Battle of Kwajalein Atoll. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 0-8032-8272-9.
- Morison, Samuel Eliot (1961). Aleutians, Gilberts and Marshalls, June 1942 – April 1944, History of United States Naval Operations in World War II. Boston: Little, Brown and Company. ASIN B0007FBB8I.
- Rottman, Gordon; Howard Gerrard (2004). The Marshall Islands 1944: "Operation Flintlock, the capture of Kwajalein and Eniwetok". Osprey Publishing. ISBN 1-84176-851-0.
- Sauer, Howard (1999). "Kwajalein". The Last Big-Gun Naval Battle: The Battle of Surigao Strait. Palo Alto, California: The Glencannon Press. ISBN 1-889901-08-3.- Firsthand account of the U.S. pre-invasion bombardment operation by a crewmember of the USS Maryland.
Further reading
- Wright III, Burton. Eastern Mandates. US Army Campaigns in World War II. United States Army Center of Military History. CMH Pub 72-23. http://www.army.mil/cmh/brochures/eastman/eastman.htm.
- Chapin, Captain John C., USMCR (Ret), Breaking the Outer Ring: Marine Landings in the Marshall Islands, Marines in World War II Commemorative Series, History and Museums Division, United States Marine Corps, 1994.
- Heinl, Robert D., and John A. Crown (1954). "The Marshalls: Increasing the Tempo". USMC Historical Monograph. Historical Division, Division of Public Information, Headquarters U.S. Marine Corps. Archived from the original on 16 November 2006. http://web.archive.org/web/20061116035646/http://ibiblio.org/hyperwar/USMC/USMC-M-Marshalls/index.html. Retrieved 2006-12-04.
- Dyer, George Carroll (1956). "The Amphibians Came to Conquer: The Story of Admiral Richmond Kelly Turner". United States Government Printing Office. Archived from the original on 21 May 2011. http://web.archive.org/web/20110521010748/http://ibiblio.org/hyperwar/USN/ACTC/index.html. Retrieved 5 May 2011.
External links
- What Makes a Battle — Moving images from Kwajalein island during battle
- Soldiers of the 184th Infantry, 7th ID in the Pacific, 1943–1945
- Animated History of The Battle for Kwajalein
Coordinates: 8°43′N 167°44′E / 8.717°N 167.733°E
The original article can be found at Battle of Kwajalein and the edit history here.