Illustration of Airway beacon, showing designated number. In this example, for units digit "1", Morse code should be ".--" (W).
An airway beacon is a rotating light on a tower once used extensively in the United States for visual navigation by airplane pilots along a specified airway corridor. Approximately 1,500 airway beacons were constructed to guide pilots from city to city,[1][2] covering 18,000 miles (29,000 km). Most of the beacons are gone, but Montana continues to maintain several in mountainous terrain.[3][4] One is preserved in Saint Paul, Minnesota[5] at the Indian Mounds Park on a bluff overlooking the Mississippi River. Recently the beacon at Grants, New Mexico was restored using original items found at other nearby sites.[6]
Many of the concrete arrows are visible from satellite pictures, even in urban settings.[7]
Light characteristics[]
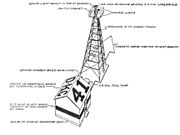
An airway beacon has two distinct light characteristics: A revolving narrow white light beam about 5 degrees wide in azimuth and a set of fixed colored course lights of about 15 degrees width.[8]
White rotating beacon[]
The rotating beacon features a 24 inch (610 mm) parabolic mirror and a 110-volt, 1 kilowatt lamp.[8] spinning at 6 rpm, creating a quick 1/10 second flash every 10 seconds. In clear weather they could be seen for 40 miles (64 km).[8][9] Montana took steps to modernize their beacons encasing newer light systems in clear domes.[10]
Red or green course lights[]
Just below the white beacon, a set of red or green course lights point along each airway route. Red lights denote an airway beacon between landing fields while green denotes a beacon adjacent or upon a landing field.[8] These course lights flash a Morse code letter identifying the beacon to the pilot. Each beacon is identified with a sequential number along the airway, and flash the red or green course lights with the Morse code of one of 10 letters: W, U, V, H, R, K, D, B, G or M. The letters represent the digits of 1 through 10 (W = 1, ..., M = 10).[8] The course lights turn on for 0.5 second for a dot, 1.5 second for a dash with a 0.5 second between each dot or dash. A pause of 1.5 seconds separates each letter.[11]
To help remember the letters and their sequence number, pilots memorized the following phrase: "When Undertaking Very Hard Routes, Keep Direction By Good Methods." The beacons were depicted on navigation charts along with their number and Morse code. As an example, beacon number 15 would have a code digit of 5 (the units digit), hence the letter R, and Morse code: "dit dah dit" (.-.).[12]
History[]

An airway beacon located in Saint Paul, Minnesota, built in 1929 and restored in the 1990s. It sits on top of a 110-foot (34 m) steel tower in Indian Mounds Park.[5]
Airway beacons were constructed by the Post Office and the Department of Commerce between 1923 and 1933.[9] The Low Frequency Radio Range system began to replace this visual system in 1929.[9] The last visual airway beacon was supposedly shut down in 1973,[9] however some airway beacons are still operating in Western Montana,[3] and are charted on the Great Falls sectional chart.[13] They are maintained by the Montana Department of Transportation Aeronautics Division.[3]
See also[]
- Lighted airway
References[]
- ↑ "Airway Beacons List - Eastern US". Roger Barnes. http://surveymarks.planetzhanna.com/airway_beacons_east.shtml. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
- ↑ "Airway Beacons List - Western U.S.". Roger Barnes. http://surveymarks.planetzhanna.com/airway_beacons_west.shtml. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Aviation in Montana". Montana Department of Transportation. http://www.mdt.mt.gov/aviation/beacons.shtml. Retrieved 2012-02-21. "Today, Montana is the only state that still utilizes part of this historic network through our rugged western mountains. Division personnel climb and maintain approximately 19 of these beacons on a regular schedule, also providing ownership and ground leases for their operation."
- ↑ Savage, Jason. "Airway Beacons". http://jasonsavagephotography.com/tag/airway-beacons/. Retrieved 5 April 2012.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Cosimini, Greg (1999-07-09). "Indian Mounds Park "Airway" Beacon". University of Minnesota. http://www.tc.umn.edu/~cosim001/beacon.html. Retrieved 2007-08-28.
- ↑ At least one beacon to be fully restored as a local museum.beacon buildings
- ↑ Aviation Navigation Arrows in Washington County, Utah
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 Wood, Charles. "How it Began". Charles Wood. http://www.navfltsm.addr.com/howitbegan.htm. Retrieved 2012-04-04.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 "The Evolution of Airway Lights and Electronic Navigation Aids". U.S. Centennial of Flight Commission. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20070930032413/http://www.centennialofflight.gov/essay/Government_Role/navigation/POL13.htm. Retrieved 2007-08-28.
- ↑ Spivey, Brenda (1993+). Airway Beacons, an Integral Part of Montana's Night VFR Navigational System: Past History, Present Service and Present Value. Embry Riddle Aeronautical University. pp. 21. http://www.eaa517.org/newsletters/AirwayBeacons.pdf.
- ↑ FAA Advisory Circular Number 170/6850-1. FAA. 1968.
- ↑ Majors, Beverly (July 7, 2009). "Beacon House was part of changes in air transportation". Associated Press. Oak Ridge, TN: OakRidger.com. http://www.oakridger.com/columnists/x135741391/Beacon-House-was-part-of-changes-in-air-transportation. Retrieved 2012-02-21.
- ↑ Rogan, Michael (2011). Airway Support Officer. "All of our airway beacons and the associated code are listed on any current Great Falls sectional[. . .]"
The original article can be found at Airway beacon and the edit history here.