- For the VII Corps of the Union Army during the American Civil War, see VII Corps (ACW).
VII Corps  Shoulder sleeve insignia of VII Corps
Shoulder sleeve insignia of VII CorpsActive 1918–19
1921–46
1950–92Country United States
Branch  United States Army
United States ArmyNickname(s) The Jayhawk Corps Engagements Gulf War Commanders Notable
commandersRobert C. Richardson Jr.
J. Lawton Collins
John Galvin
Frederick M. Franks, Jr.Insignia Distinctive unit insignia 
Shoulder sleeve insignia prior to April 28, 1944 
U.S. Corps (1939 - Present) Previous Next VI Corps (United States) VIII Corps (United States) The VII Corps of the United States Army was one of the two principal corps of the United States Army Europe during the Cold War. Activated in 1918 for World War I, it was reactivated for World War II and again during the Cold War. During both World War II and the Cold War it was subordinate to the Seventh Army, or USAREUR and was headquartered at Kelley Barracks in Stuttgart, West Germany, from 1951 until it was redeployed to the US and inactivated in 1992.
World War I[]
VII Corps was organized at the end of World War I on 19 August 1918, at Remiremont, France and was inactivated in 1919.
World War II[]
VII Corps was reactivated at Fort McClellan, Alabama 25 November 1940 and participated in the Louisiana Maneuvers staged as the US Army prepared for World War II. In late December 1941, VII Corps HQ was moved to San Jose, California as part of the Western Defense Command and as it continued to train and prepare for deployment.[1]
Its first return to continental Europe took place on D-Day in June 1944, as one of the two assault corps for the U.S. First Army during Operation Overlord, targeting Utah Beach via amphibious assault. For Overlord, the 82nd and 101st Airborne Divisions were attached to VII Corps.[2] After the Battle of Normandy the airborne units were assigned to the newly created XVIII Airborne Corps. Subsequently, VII Corps participated in many battles during the advance across France and then invaded Germany until the surrender of the Third Reich in May 1945. The corps was inactivated in 1946.
Battle of Normandy[]

Major General J. Lawton Collins, VII Corps, describes the taking of Cherbourg to General Omar Bradley, First Army.
For the Normandy Operation, VII Corps was part of 21st Army Group under the command of General Bernard Montgomery and the U.S. First Army commanded by Lieutenant General Courtney Hodges. The Corps was commanded by Major General J. Lawton Collins.
VII Corps led the initial assault of Operation Cobra, the First Army-led offensive as part of the breakout of the Normandy area. Its success is credited with changing the war in France from high-intensity infantry combat to rapid maneuver warfare.
Assigned Units and Commanders[]
- 4th Infantry Division, Maj.Gen. Raymond O. Barton
- 8th Infantry Col. James A. Van Fleet
- 12th Infantry Col. Russell P. Reeder (11 June)
- Lt. Col. Hervey Tribolet
- 22nd Infantry Col. Hervey A. Tribolet
- Col. Robert T. Foster (26 June)
- 9th Infantry Division, Maj.Gen. Manton S. Eddy
- 39th Infantry Col. Harry A. "Paddy" Flint
- 47th Infantry Col. George W. Smythe
- 60th Infantry Col. Frederick J. de Rohan
- 79th Infantry Division, Maj.Gen. Ira T. Wyche
- 313th Infantry Col. Sterling A. Wood
- 314th Infantry Col. Warren A. Robinson
- 315th Infantry Col. Porter P. Wiggins
- Col. Bernard B. McMahon (24 June)
- 82nd Airborne Division, Maj.Gen. Matthew B. Ridgway
- 505th Parachute Infantry Col. William E. Ekman
- 507th Parachute Infantry Col. George V. Millett, Jr.
- Col. Edson D. Raff (15 June)
- 508th Parachute Infantry Col. Roy E. Lindquist
- 325th Glider Infantry Col. Harry L. Lewis
- 90th Infantry Division, Brig.Gen. Jay W. MacKelvie
- 357th Infantry Col. Philip De Witt Ginder
- Col. John W. Sheehy (13 June)
- Lt. Col. Charles M. Schwab (15 June)
- Col. George B. Barth (17 June)
- 358th Infantry Col. James V. Thompson
- Col. Richard C. Partridge (16 June)
- 359th Infantry Col. Clark K. Fales
- 357th Infantry Col. Philip De Witt Ginder
- 101st Airborne Division, Maj.Gen. Maxwell D. Taylor
- 501st Parachute Infantry Col. Howard R. Johnson
- 502nd Parachute Infantry Col. George V. H. Moseley, Jr. (WIA 6 June)
- Lt. Col. John H. Michaelis (6 June)
- 506th Parachute Infantry Col. Robert F. Sink
- 327th Glider Infantry Col. George S. Wear
- Col. Joseph H. Harper (10 June)
- 4th Cavalry Group (Mechanized), Col. Joseph M. Tully
- 4th Cavalry Squadron Lt. Col. E. C. Dunn
- 24th Cavalry Squadron Lt. Col. F. H. Gaston, Jr.
- 6th Armored Group, Col. Francis F. Fainter
- 70th Tank Battalion Lt. Col. John C. Welborn
- 746th Tank Battalion Lt. Col. C. G. Hupfer
Battle casualties, 6 June – 1 July 1944
Unit Total Killed Wounded Missing Captured All Units 22,119 2,811 13,564 5,665 79 4th Inf Division 5,452 844 3,814 788 6 9th Inf Division 5,438 301 2,061 76 0 79th Inf Division 2,438 240 1,896 240 0 90th Inf Division 2,376 386 1,979 34 0 82d A/B Div. 4,480 457 1,440 2,571 12 101st A/B Div. 4,670 546 2,217 1,907 0 Corps Troops 304 37 157 49 61 Source: VII Corps, G-1 Reports, June 1944
Cold War[]

VII Corps Cold War NATO assignment.

VII Corps Garrison Footprint in the 1980s
From reactivation in 1950 and throughout the Cold War, the corps guarded part of NATO's front with the Warsaw Pact. Headquartered in Stuttgart at Kelley Barracks it was one of the two main US combat formations in Germany along with V Corps, which was headquartered in Frankfurt am Main at Abrams Building. At the end of the Cold War, VII Corps would have commanded the following units in case of war:

VII US Corps 1989
- VII Corps, Stuttgart
- 1st Armored Division, Ansbach
- 1st Infantry Division (Mechanized), Fort Riley, Kansas, OPERATION REFORGER unit. POMCUS Set 1 depots at Mannheim
- 1st Canadian Infantry Division (Mechanized), Kingston, Ontario
- 3rd Infantry Division (Mechanized), Würzburg
- 2nd Armored Cavalry Regiment, Nürnberg
- VII Corps Artillery, Stuttgart
- 17th Field Artillery Brigade, Augsburg
- 72nd Field Artillery Brigade, Wertheim
- 210th Field Artillery Brigade, Herzogenaurach
- 11th Combat Aviation Brigade, Illesheim
- 7th Engineer Brigade, Kornwestheim
- 14th Military Police Brigade, Ludwigsburg
- 2nd Support Command, Nellingen
- 207th Military Intelligence Brigade, Ludwigsburg
- 38th Infantry Division (National Guard), Indianapolis, Indiana
- 602nd Air Support Operations Group, USAF [4] Stuttgart

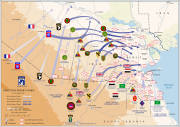
VII Corps Gulf War Map.
Gulf War[]
After Saddam Hussein's troops invaded Kuwait in 1990, the corps was deployed to Saudi Arabia as part of the second major wave of deployments of American forces. Its presence took US forces in theatre from a force capable of defending Saudi Arabia to a force capable of ejecting Iraqi troops from Kuwait.

Captured Iraqi T-72 Tank at VII Corps Cold War HQ, Kelley Barracks.

An Iraqi Republican Guard tank destroyed by Task Force 1-41 Infantry during the 1st Gulf War, February 1991.
In the Gulf War, VII Corps was probably the most powerful formation of its type ever to take to the battlefield. Normally, a corps commands three divisions when at full strength, along with other units such as artillery of various types, corps-level engineers and support units. However, VII Corps had far more firepower under its command.
Its principal full strength fighting formations were U.S. 1st Armored Division, U.S. 3rd Armored Division and U.S. 1st Infantry Division. 2nd Armored Division (Forward) would be assigned to the 1st Infantry division as its third maneuver brigade.[5] Its Task Force 1-41 Infantry would be the spearhead of VII Corps.[6] It would perform the breach of initial Iraqi defensive positions.[7] In addition, the corps had U.S. 2nd Cavalry Regiment to act as a scouting force, and two further heavy divisions; US 1st Cavalry Division and British 1st Armoured Division, as well as the 11th Aviation Group.[8][9][10] Although both 1st Cavalry Division and 1st Armoured Division had only two maneuver brigades, they were still immensely powerful formations in their own right.
VII corps was originally deployed to provide an offensive option if needed. In the 100-hour war they were given a force mission: To wipe out the Iraqi Republican Guard's Heavy Divisions. That meant that the 1st Infantry Division had to make a forced entry to make room for the British attack on the right wing and to secure the main forces advance on the left. That attack force was led by the 2nd Armored Cavalry Regiment and Task Force 1-41 Infantry followed by the other two brigades of the 1st Infantry Division.[11] The 1st Armored Division would head north to engage the Iraqi Republican Guard in the Battle of Medina Ridge.[12] The 3rd Armored Division would protect the flank of the 1st Infantry Division. That gave VII Corps commander General Frederick M. Franks, Jr. a three division strike force to confront several Iraqi Armored Divisions. After the corps had turned 90 degrees east according to FRAGPLAN 7 and after the Cavalry Regiment had fought the single sided Battle of 73 Easting the three Divisions (plus the British on the right wing) fought one of the most one sided battles in the history of the US Army.[13]
VII Corps cut a swath through Iraqi forces. It advanced with U.S. XVIII Airborne Corps on its left wing and Arab forces on its right wing. Led by Task Force 1-41 Infantry it pulverized all Iraqi forces that tried to stand and fight and destroyed a good proportion of the Iraqi Republican Guard divisions.[14] This confrontation was known as the Battle of Norfolk.[15] VII Corps' attack cost about 341 US and British soldiers' lives. But it destroyed several divisions including the Medina and the Tawakalna Republican Guards division along with support units. It also destroyed most of the Iraqi VII Corps that had guarded the frontline as well as other units. The Battle of 73 Easting was studied as a textbook armored battle within the US armored units. 'Virtually every manoeuvre battalion in the 1st and 3rd Armored Divisions, 1st Inf Div (M), and 2 ACR received the Valorous Unit Award.[16] In addition, 'six of the ten VII Corps manoeuvre brigade headquarters that saw substantial combat against the Republican Guard received the VUA in contravention of the spirit, if not the letter, of AR672-5-1's guidance that '[o]nly on rare occasions will a unit larger than a battalion qualify for award of the VUA.'[17]
During the Gulf War VII Corps destroyed as many as 1,350 Iraqi tanks, 1,224 armored troop carriers, 285 artillery pieces, 105 air defense systems and 1,229 trucks.[18] VII Corps lost no more than 36 armored vehicles to enemy fire, and suffered a total of 47 dead and 192 wounded.[19]
Redeployment and inactivation[]
After the fighting was over, most VII Corps units were redeployed directly to the United States for reassignment or inactivation. VII Corps HQ returned to Germany and was disbanded as part of the post-Cold War American defense spending cuts. Some VII Corps units remained in Germany and were reassigned to V Corps or USAREUR. A farewell ceremony was held in downtown Stuttgart at Schlossplatz, where the VII Corps colors were retired on March 18, 1992.[20] The official inactivation was held at Fort McPherson, Ga., in April 1992.[21]
Commanders during the Cold War and Gulf War[]
- Maj. Gen. Withers A. Burress - June 1951 - December 1952
- Maj. Gen. James M. Gavin - December 1952 - March 1954
- Lt. Gen. Henry I. Hodes - March 1954 - February 1955
- Lt. Gen. George H. Decker - February 1955 - May 1956
- Maj. Gen. Halley G. Maddox - June - July 1956
- Lt. Gen. John F. Uncles - August 1956 - August 1958
- Lt. Gen. Gordon B. Rogers - September 1958 - October 1959
- Lt. Gen. Guy S. Meloy, Jr. - October 1959 - January 1961
- Lt. Gen. John C. Oakes - January 1961 - April 1962
- Lt. Gen. C. H. Bonesteel III - April 1962 - August 1963
- Lt. Gen. Louis W. Truman - September 1963 - July 1965
- Lt. Gen. Frank T. Mildren - July 1965 - May 1968
- Lt. Gen. Donald V. Bennett - June 1968 - September 1969
- Lt. Gen. George G. O'Connor - October 1969 - February 1971
- Lt. Gen. Fillmore K. Mearns - February 1971- March 1973
- Lt. Gen. George S. Blanchard - March 1973 - June 1975
- Lt. Gen. Frederick J. Kroesen - July 1975 - October 1976
- Lt. Gen. David E. Ott - October 1976 - October 1978
- Lt. Gen. Julius W. Becton, Jr. - October 1978 - June 1981
- Lt. Gen. William J. Livsey - June 1981 - July 1983
- Lt. Gen. John R. Galvin - July 1983 - February 1985
- Lt. Gen. Andrew P. Chambers - February 1985 - July 1987
- Lt. Gen. Ronald L. Watts - July 1987 - August 1989
- Lt. Gen. Frederick M. Franks Jr. - August 1989 - June 1991
- Lt. Gen. Michael Spiglemire - August 1991 - 1992 (Inactivation)[22]
References[]
- ↑ "Mission Accomplished Story of the VII Corps". Xixcorps.nl. http://www.xixcorps.nl/Mission_Accomplished_Story_of_the_VII_Corps.htm. Retrieved 2013-06-24.
- ↑ "VII Corps in WWII". Vii-corps.org. http://www.vii-corps.org/WWII/WWII.htm. Retrieved 2013-06-24.
- ↑ "VII Corps in WWII". Vii-corps.org. http://www.vii-corps.org/WWII/WWII.htm. Retrieved 2013-06-24.
- ↑ "602nd Air Support Operations Group". Air Force: We served Together. http://airforce.togetherweserved.com/usaf/servlet/tws.webapp.WebApp?cmd=PublicUnitProfile&type=Unit&ID=15513.
- ↑ Dinackus P.4–10
- ↑ VUA Citation
- ↑ VUA Citation
- ↑ VUA Citation
- ↑ Bourque, p.275
- ↑ Bourque, p.377
- ↑ VUA Citation
- ↑ Bourque, p.355
- ↑ name=middleeast
- ↑ VUA Citation.
- ↑ Dinackus P.4–10
- ↑ VUA Citation
- ↑ Thomas D. Dinackus, 2000, 14-4 and 14-5.
- ↑ https://www.comw.org/rma/fulltext/victory.html
- ↑ https://www.comw.org/rma/fulltext/victory.html
- ↑ http://www.usarmygermany.com/Communities/Stuttgart/Images_The%20Citizen%201.htm
- ↑ http://www.stuttgartcitizen.com/stuttgart-employee-reflects-on-46-years-of-service/
- ↑ "USAREUR Units & Kasernes, 1945 - 1989". Usarmygermany.com. http://www.usarmygermany.com/Sont.htm?http&&&www.usarmygermany.com/Units/Corps/USAREUR_VIICorps.htm. Retrieved 2013-06-24.
- Clancy, Tom (2007). Into The Storm: A Study in Command. Berkley Trade.
- Ryan, John (May 1998). Battle Command in the Storm: Lieutenant General Franks and VII Corps. School of Advanced Military Studies United States Army Command and General Staff College.
- Casey, Melanie (13 July 2004), "From Helenen Kaserne to Kelley Barracks", Stuttgart Citizen (Stuttgart, Germany): P 10
- Draft Report The Battle of 73 Easting, 26 February 1991, a historical introduction to a simulation. Krause, Col Michael, US Army Center of Military History, 2 May 1991.
- Jayhawk! The VII Corps in the Persian Gulf War, Stephen A. Borque, Center of Military History Publication 70-73-1, Washington, DC, 2002.
- "Desert Storm/Shield Valorous Unit Award (VUA) Citations". US Army Center of Military History. http://www.history.army.mil/html/forcestruc/vua_citations.html. Retrieved 26 December 2014.
- Bourque, Stephen A.; Burdan, John (2007). The road to Safwan the 1st Squadron, 4th Cavalry in the 1991 Persian Gulf War. Denton, Tex: University of North Texas Press. ISBN 9781574412321.
External links[]
- GlobalSecurity.org: VII Corps
- Cold War History of VII Corps
- World War II operations history of VII Corps
- History site for VII Corps
- Order of Battle information on VII Corps
All or a portion of this article consists of text from Wikipedia, and is therefore Creative Commons Licensed under GFDL.
The original article can be found at VII Corps (United States) and the edit history here.
Advertisement
347,158
pages
VII Corps (United States)
Advertisement