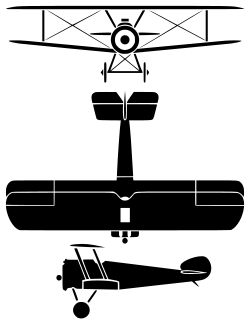
| Sopwith Camel | |
|---|---|
| Role | Biplane fighter |
| Manufacturer | Sopwith Aviation Company |
| Designer | Herbert Smith[1] |
| First flight | 22 December 1916 |
| Introduction | June 1917 |
| Primary users | RFC (RAF) RNAS, AAF |
| Number built | 5,490 |
The Sopwith Camel was a British First World War single-seat biplane fighter introduced on the Western Front in 1917. Manufactured by Sopwith Aviation Company, it had a short-coupled fuselage, heavy, powerful rotary engine, and concentrated fire from twin synchronized machine guns. Though difficult to handle, to an experienced pilot it provided unmatched manoeuvrability. A superlative fighter, the Camel was credited with shooting down 1,294 enemy aircraft, more than any other Allied fighter of the war. It also served as a ground-attack aircraft, especially near the end of the conflict, when it was outclassed in the air-to-air role by newer fighters.
Design and development[]
Intended as a replacement for the Sopwith Pup,[2] the Camel prototype was first flown by Harry Hawker at Brooklands on 22 December 1916, powered by a 110 hp Clerget 9Z. Known as the "Big Pup" early on in its development, the biplane design was structurally conventional for its time, featuring a box-like fuselage structure, an aluminium engine cowling, plywood-covered panels around the cockpit, and fabric-covered fuselage, wings and tail. For the first time on an operational British-designed fighter, two .303 in (7.7 mm) Vickers machine guns were mounted directly in front of the cockpit, firing forward through the propeller disc with synchronisation gear. A metal fairing over the gun breeches, intended to protect the guns from freezing at altitude, created a "hump" that led to the name Camel.[2] The bottom wing was rigged with 3° dihedral but the top wing had no dihedral, so that the gap between the wings was less at the tips than at the roots. This was done at the suggestion of Fred Sigrist, the Sopwith works manager, in order to simplify construction. Approximately 5,490 Camels were built.[3]
Unlike the preceding Pup and Triplane, the Camel was generally considered difficult to fly. The type owed its extreme manoeuvrability and its difficult handling to the close placement of the engine, pilot, guns and fuel tank (some 90% of the weight of the aircraft) within the front seven feet of the aircraft, coupled with the strong gyroscopic effect of the rotary engine. The Camel soon gained an unfortunate reputation with student pilots. The Clerget engine was particularly sensitive to fuel mixture control and incorrect settings often caused the engine to choke and cut out during take-off. Many crashed due to mishandling on take-off when a full fuel tank affected the centre of gravity. In level flight, the Camel was markedly tail-heavy. Unlike the Sopwith Triplane, the Camel lacked a variable incidence tailplane, so that the pilot had to apply constant forward pressure on the control stick to maintain a level attitude at low altitude. The aircraft could also be rigged so that at higher altitudes it was able to be flown "hands off." A stall immediately resulted in a particularly dangerous spin.
Operational history[]
Western front[]

Replica of Camel F.I flown by Lt. George A. Vaughn Jr., 17th Aero Squadron

This aircraft is currently displayed at the National Museum of the United States Air Force.
The type entered squadron service in June 1917 with No. 4 Squadron of the Royal Naval Air Service, near Dunkirk. The following month, it became operational with No. 70 Squadron of the Royal Flying Corps. By February 1918, 13 squadrons were fully equipped with the Camel.
The Camel proved to have a good margin of superiority over the Albatros D.III and D.V and offered heavier armament and better performance than the Pup and Triplane. In the hands of an experienced pilot, its manoeuvrability was unmatched by any contemporary type. Its controls were light and sensitive. The Camel turned rather slowly to the left, which resulted in a nose up attitude due to the torque of the rotary engine. But the engine torque also resulted in the ability to turn to the right in half the time of other fighters,[4] although that resulted in more of a tendency towards a nose down attitude from the turn. Because of the faster turning capability to the right, to change heading 90° to the left, many pilots preferred to do it by turning 270° to the right.
Agility in combat made the Camel one of the best-remembered Allied aircraft of the First World War. It was said in jest to offer a choice between a "wooden cross, red cross, and Victoria Cross."[citation needed] Together with the S.E.5a and the SPAD S.XIII, the Camel helped to establish the Allied aerial superiority that lasted well into 1918.
Major William Barker's Sopwith Camel (serial no. B6313, the aircraft in which he scored the majority of his victories,[5]) became the most successful fighter aircraft in the history of the RAF, shooting down 46 aircraft and balloons from September 1917 to September 1918 in 404 operational hours flying. It was dismantled in October 1918. Barker kept the dashboard watch as a memento, but was asked to return it the following day.
Home defence and night fighting[]
An important role for the Camel was home defence. The RNAS flew a number of Camels from Eastchurch and Manston airfields against daylight raids by German Gotha bombers from July 1917. The public outcry against these raids and the poor response of London's defences resulted in the RFC diverting Camel deliveries from France to home defence, with 44 Squadron RFC reforming on the Camel in the home defence role in July 1917.[6] When the Germans switched to night attacks, the Camel proved capable of being safely flown at night, and the home defence aircraft were modified with navigation lights to serve as night fighters. A number of Camels were more extensively modified as night fighters, with the Vickers machine guns being replaced by overwing Lewis guns, with the cockpit being moved rearwards so the pilot could easily reload the guns. This modification, which became known as the "Sopwith Comic" allowed the guns to be fired without affecting the night vision of the pilots, and allowed the use of new and more effective incendiary ammunition that was considered unsafe to fire from synchronised Vickers guns.[7][8][N 1] By March 1918, the home defence squadrons were equipped with the Camel, with seven home defence squadrons flying Camels by August 1918.[10] Camels were also used as night fighters over the Western Front, with 151 Squadron intercepting German night raids over the front, and carrying out night intruder missions against German airstrips, claiming 26 German aircraft shot down in five months of operations.[11]
Ground attack[]
By mid-1918, the Camel was becoming limited, especially as a day fighter, by its slow speed and comparatively poor performance at altitudes over 12,000 ft (3,650 m). However, it remained useful as a ground-attack and infantry support aircraft. During the German offensive of March 1918, flights of Camels harassed the advancing German Army, inflicting high losses (and suffering high losses in turn) through the dropping of 25 lb (11 kg) Cooper bombs and ultra-low-level strafing. The protracted development of the Camel's replacement, the Sopwith Snipe, meant that the Camel remained in service until the Armistice.
In summer 1918, a 2F.1 Camel (N6814) was used in trials as a parasite fighter under Airship R23
Variants[]
Camels were powered by several rotary engines.
- 130 hp Clerget 9B Rotary (standard powerplant)
- 140 hp Clerget 9Bf Rotary
- 110 hp Le Rhône 9J Rotary
- 150 hp Bentley BR1 rotary (gave best performance – standard for R.N.A.S. machines)
- 100 hp Gnome Monosoupape 9B-2 Rotary
- 150 hp Gnome Monosoupape 9N Rotary
Engine variants[]
With rotary engines, the crankshaft remain static and the cylinders, crankcase and attached propeller rotate around it. The torque produced by this rotating mass produces a significant "pull" to the right. In the hands of an experienced pilot, this characteristic could be exploited to give exceptional manoeuvrability in a dogfight. A 3/4 turn to the right could be done in the same time as a 1/4 turn to the left.
The Gnome "mono" engines did not have throttles and were at full "throttle" while the ignition was on – they could be "throttled" with a selector switch which cut the ignition to some of the cylinders to reduce power for landing. The Clerget, Le Rhone and BR1 had throttles, although reducing power involved simultaneously adjusting the mixture and was not straightforward, so it became common during landing to "blip" the engine (turn the ignition off and on) using a control column-mounted ignition switch, the blip switch, to reduce power.
Sopwith Camel F.1[]
- Single-seat fighter aircraft.
- The main production version. Armed with twin synchronised Vickers guns.

A Sopwith 2F1 Camel naval variant, flown by Flight Sub-lieutenant Stuart Culley when he shot down Zeppelin L 53, at the Imperial War Museum, London. Note non-standard armament of two Lewis guns in fixed, inaccessible mount over top wing.
Sopwith Camel 2F.1[]
- Shipboard fighter aircraft.
- Slightly shorter wingspan
- One Vickers gun replaced by an overwing Lewis gun
- Bentley BR1 as standard engine
Sopwith Camel "Comic" Night fighter[]
The twin Vickers guns were replaced with two Lewis guns on Foster mountings firing forward over the upper wing, since the muzzle flash of the Vickers guns tended to blind the pilot. To allow the pilot to reload the guns, the pilot seat was moved about 12 inches (30 cm) to the rear; to compensate for this, the fuel tank was moved forward.[12] Served with Home Defence Squadrons against German air raids. The "Comic" nickname was of course unofficial, and was shared with the night fighter version of the Sopwith 1½ Strutter.
F.1/1[]
- Version with tapered wings.
(Trench Fighter) T.F.1[]
- Experimental-only trench fighter.
- Downward angled machine guns for efficient strafing
- Armour plating for protection
(See also Sopwith Salamander)
Operators[]

Belgian Camel preserved at the Royal Museum of the Armed Forces and of Military History in Brussels
- Australian Flying Corps
- No. 4 Squadron AFC in France.
- No. 5 (Training) Squadron AFC in the United Kingdom.
- No. 6 (Training) Squadron AFC in the United Kingdom.
- No. 8 (Training) Squadron AFC in the United Kingdom.
- Polish Air Force operated 1 Camel post-war (1921)
- Soviet Air Force - Postwar.
Survivors[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sopwith Camel museum aircraft. |

Sopwith Camel at the Royal Air Force Museum
There are seven original Sopwith Camels left.
- One was displayed in the Aerospace Education Center in Little Rock, Arkansas, which was closed as of December 2010 and the Camel sold to help pay debts. The Camel was sold privately and moved to a museum in New Zealand.[18]
- One, restored to near-flying condition, is at the Brussels Air Museum Restoration Society (BAMRS) in Brussels, Belgium.
- A Camel F.1 (s/n B 7280) can be found at the Polish Aviation Museum. This Camel first flew in Royal Naval Air Service and then in the Royal Flying Corps. Two pilots who flew this aircraft shot down 11 German aircraft.
- N6812, a William & Beardmore built 2F1 Camel, was flown by Flight Sub Lieutenant Stuart Culley on 11 August 1918 when he shot down Zeppelin LZ100; it is on display at the Imperial War Museum in London.[19]
- A Camel 2F1 N8156 (RAF) is currently on display at the Canadian Aviation Museum. Manufactured in 1918 by Hooper and Company Ltd., Great Britain, it was purchased by the RCAF in 1924 and last flew in 1967. It is on static display.[20]
- F.1 Camel B6291 restored to flying condition, is part of the Javier Arango Collection, in Paso Robles, California. It was previously owned by Al Letcher.
- A Boulton & Paul built F1 F6314 is on display at the Milestone of Flight exhibition at the Royal Air Force Museum, London,[21] painted to represent an aircraft coded B of No. 65 Squadron RAF.[22]
Reproductions[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sopwith Camel replicas. |
- In 1969 Slingsby built a flyable Type T.57 Sopwith Camel reproduction powered by a 145 hp Warner Scarab engine for use in a Biggles film. This aircraft is on display at the Fleet Air Arm Museum, Yeovilton painted as B6401.[23][24]
- A reproduction Sopwith F.1 Camel is on display at the National Museum of the United States Air Force in Dayton, Ohio. This aircraft was built by museum personnel from original First World War factory drawings and was completed in 1974. It is painted and marked as the Camel flown by Lt. George A. Vaughn Jr. while flying with the 17th Aero Squadron.[25]
- The Sopwith Camel on display at the Cavanaugh Flight Museum in Addison, TX is a full scale flying replica built by Dick Day from original World War I factory drawings. The aircraft is fitted with original instruments, machine guns and an original Gnome rotary engine (something very rare in replicas). It is painted in the scheme of the World War I flying ace Captain Arthur Roy Brown, a Canadian flying with the Royal Air Force.
- In 1977, a flyable reproduction was built for Leisure Sport Ltd by the late Viv Bellamy at Lands End. Painted to represent B7270 of 209 Squadron, RAF, the machine which Captain Roy Brown flew when officially credited with downing Baron Manfred von Richthofen, it has a Clerget rotary engine of 1916 and was registered as G-BFCZ until 2003. First seen at Brooklands Museum in January 1988 for Sir Thomas Sopwith’s 100th birthday celebrations, it was purchased by the Museum later that year, can be taken by road for exhibition elsewhere and is ground run regularly.
- Old Rhinebeck Aerodrome flies a reproduction Camel completed in 1992 with a 160 hp Gnome Monosoupape model 9N rotary, built by Nathaniel deFlavia and Cole Palen. It replaced one of the Dick-Day built and flown Camel reproductions formerly flown at Old Rhinebeck by Mr. Day in their weekend vintage airshows, which had left the Aerodrome's collection some years earlier.
- N8343 constructed by Dick Day, is part of the Javier Arango Collection, in Paso Robles, California. Powered by a 160 h.p. Gnome Monosoupape rotary. It is regularly flown.
- Another reproduction is on display at the Evergreen Aviation museum.
- B3889 is part of The Vintage Aviator Collection, L.T.D., in Masterton, New Zealand. It was originally built by Carl Swanson for Gerry Thornhill. It is often flown. Powerplant is a 160 hp Gnome Monosoupape rotary engine.
- New reproductions are currently under construction by 1) the Northern Aeroplane Workshops for the Shuttleworth Collection, in England.[26] and 2) another is under construction at the Great War Flying Museum, in Brampton, Ontario, Canada.
- A replica of the Camel is being built in the United States by Koz Aero LLC, based on original factory drawings, using many original parts, including an original engine and instruments.[27]
- A replica Sopwith F.1 Camel B5577 is on display at Montrose Air Station Heritage Centre, Angus, Scotland.
Specifications (F.1 Camel)[]

Replica Sopwith Camel under construction, showing structure, at Shuttleworth Uncovered September 2013
Data from Quest for Performance[28]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 18 ft 9 in (5.71 m)
- Wingspan: 28 ft 0 in (8.53 m)
- Height: 8 ft 6 in (2.59 m)
- Wing area: 231 ft² (21.46 m²)
- Empty weight: 930 lb (420 kg)
- Loaded weight: 1,455 lb (660 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Clerget 9B 9-cylinder Rotary engine, 130 hp (97 kW)
- Zero-lift drag coefficient: 0.0378
- Drag area: 8.73 square feet (0.811 m2)
- Aspect ratio: 4.11
Performance
- Maximum speed: 115 mph (185 km/h)
- Stall speed: 48 mph (77 km/h)
- Range: 300 mi ferry (485 km)
- Service ceiling: 21,000 ft (6,400 m)
- Rate of climb: 1,085 ft/min (5.5 m/s)
- Wing loading: 6.3 lb/ft² (30.8 kg/m²)
- Power/mass: 0.09 hp/lb (150 W/kg)
- Lift-to-drag ratio: 7.7
Armament
- Guns: 2× 0.303 in (7.7 mm) Vickers machine guns
Notable appearances in media[]
Snoopy
piloting his
"Sopwith Camel".
The Camel appears in literature and popular media as:
- One of the aircraft flown by Canadian pilot Arthur Roy Brown in the 2008 movie The Red Baron.
- The single-seater scout flown by the Royal Flying Corps Squadron in the semi-autobiographical, First World War air combat book Winged Victory written by Victor Maslin Yeates.
- The fighter flown by Biggles in the novels by W.E. Johns during the character's spell in 266 Squadron during the First World War. He also wrote a book, The Camels Are Coming.
- The "plane" of Snoopy in the Peanuts comic strip, when he imagines himself as a World War I flying ace and the nemesis of the Red Baron.
- The type of aircraft flown in the First World War by John and Bayard Sartoris in William Faulkner's Flags in the Dust.[N 2]
- In the Percy Jackson book The Titan's Curse, Annabeth's father, a historian, uses a restored and modified Sopwith Camel to aid the heroes at one point during the novel.
- Robert Redford flew a Sopwith Camel during the climactic aerial battle scene in the 1975 film "The Great Waldo Pepper".
See also[]
- Albatros D.V
- Fokker D.VII
- Fokker Dr.I
- S.E.5
- SPAD S.XIII
- List of aircraft of the Royal Air Force
- Clayton & Shuttleworth
References[]
Notes[]
- ↑ The ammunition in question was the RTS (Richard Thelfall and Sons) round, a combined incendiary and explosive round with a nitroglycerin and phosphorus filling. While more effective than earlier incendiary bullets like the phosphorus filled Buckingham bullet, they required careful handling, and were initially banned from synchronised weapons, both because of fears about the consequences of bullets striking the propeller of the fighter, and to prevent cooking off of the sensitive ammunition in the chambers of the Vickers guns, which fired from a closed bolt - a required feature for guns used in synchronized mounts - where heat could build up much quicker than in the open bolted Lewis gun.[7][9]
- ↑ Quote: "Under fire from a pupil of Richthofen (the Red Baron), John's Camel caught fire over occupied France. Bayard's last sight of his twin brother was of John jumping out of his fighter feet first. Faulkner also wrote about the Camel (and Sartoris) in his famous story All the Dead Pilots."
Citations[]
- ↑ Mason 1992, p. 89.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Bruce Flight 22 April 1955, p. 527.
- ↑ Bruce Flight 29 April 1955, p. 563.
- ↑ Clark 1973, p. 134.
- ↑ Ralph 1999, p. 80.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Davis 1999, p. 96.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Davis 1999, p. 97.
- ↑ Bruce 1968, p. 151, 153.
- ↑ Williams and Gustin 2003, pp. 11, 14.
- ↑ Davis 1999, p. 98.
- ↑ Davis 1999, pp. 98–99.
- ↑ Mason 1992, p. 91.
- ↑ Davis 1999, p. 102.
- ↑ "9 Bomb Squadron (ACC)." Air Force Historical Research Agency. Retrieved: 19 December 2010.
- ↑ "17 Weapons Squadron (ACC)." Air Force Historical Research Agency. Retrieved: 19 December 2010.
- ↑ "27 Fighters Squadron (ACC)." Air Force Historical Research Agency. Retrieved: 19 December 2010.
- ↑ "37 Bomb Squadron (ACC)."Air Force Historical Research Agency. Retrieved: 19 December 2010.
- ↑ "Closed center sells rare planes to pay bills." guardonline.com, 16 March 2011.
- ↑ Ellis 2008, p. 148.
- ↑ "Sopwith 2F.1 Camel." Canada Aviation and Space Museum. Retrieved: 19 December 2010.
- ↑ Ellis 2008, p. 145.
- ↑ "Individual History: Sopwith F.1 Camel F6314/9206M." Royal Air Force Museum, 2007. Retrieved: 19 December 2010.
- ↑ Jackson 1988, p. 349.
- ↑ ""Sopwith Camel (replica) ('B6401')." Fleet Air Arm Museum. Retrieved: 14 November 2008.
- ↑ United States Air Force Museum 1975, p. 12.
- ↑ "Sopwith Camel." Shuttleworth Collection. Retrieved: 19 December 2010.
- ↑ Kozura, Tom. "Sopwith F.1 Camel." kozaero.com. Retrieved: 24 December 2011.
- ↑ Loftin, LK, Jr. "Quest for Performance: The Evolution of Modern Aircraft. NASA SP-468". NASA. Retrieved: 22 April 2006.
Bibliography[]
- Bruce, J.M. "Sopwith Camel: Historic Military Aircraft No 10: Part I." Flight, 22 April 1955, pp. 527–532.
- Bruce, J.M. "Sopwith Camel: Historic Military Aircraft No 10: Part II." Flight, 29 April 1955. pp. 560–563.
- Bruce, J.M. War Planes of the First World War: Volume Two Fighters. London:Macdonald, 1968. ISBN 0 356 0143 8.
- Clark, Alan. Aces High: The War In The Air Over The Western Front 1914 - 1918. New York: G. P. Putnam's Sons, 1973. ISBN 0-297-99464-6.
- Davis, Mick. Sopwith Aircraft. Ramsbury, Malborough, UK: The Crowood Press, 1999. ISBN 1-86126-217-5.
- Ellis, Ken. Wrecks & Relics, 21st edition. Manchester, UK: Crecy Publishing, 2008. ISBN 978-0-85979-134-2.
- Jackson, A.J. British Civil Aircraft 1919-1972: Volume III. London: Putnam, 1988. ISBN 0-85177-818-6.
- Mason, Francis K. The British Fighter. London: Putnam, 1992. ISBN 0 85177 852 6
- Ralph, Wayne. Barker VC: The Classic Story of a Legendary First World War Hero. London: Grub Street, 1999. ISBN 1-902304-31-4.
- Robertson, Bruce. Sopwith: The Man and His Aircraft. London: Harleyford, 1970. ISBN 0-900435-15-1.
- Sturtivant, Ray and Gordon Page. The Camel File. Tunbridge Wells, Kent, UK: Air-Britain (Historians) Ltd., 1993. ISBN 0-85130-212-2.
- United States Air Force Museum Guidebook. Wright-Patterson AFB, Ohio: Air Force Museum Foundation, 1975.
- Williams, Anthony G. and Emmanuel Gustin. Flying Guns: World War I and its Aftermath 1914–32. Ramsbury, Wiltshire: Airlife, 2003. ISBN 1-84037-396-2.
- Winchester, Jim, ed. "Sopwith Camel." Biplanes, Triplanes and Seaplanes (Aviation Factfile). London: Grange Books plc, 2004. ISBN 1-84013-641-3.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sopwith Camel. |
- Camel photos and links to museums with Camels
- Canadian Aviation Museum Camel
- Sopwith fighters in Russia
| ||||||||||||||
The original article can be found at Sopwith Camel and the edit history here.